What is green IT?
Green IT (green information technology) is the practice of creating and using environmentally sustainable computing.
Green IT aims to minimize the negative effect of IT operations on the environment by designing, manufacturing, operating and disposing of PCs and computer-related products in an environmentally friendly manner. The motives behind green IT practices include reducing the use of hazardous materials, maximizing energy efficiency during a product’s lifetime, and promoting the biodegradability of unused and outdated products.
The concept of green IT emerged in 1992 when the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency launched Energy Star, a voluntary labeling program identifies products that offer superior energy efficiency. Organizations and consumers that use Energy Star products save money and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Other components of green IT include the redesign of data centers and the increased use of virtualization, green networking and cloud computing.
Importance of green IT
Green IT is important for several reasons, including the following three:
- Climate change. Enterprise IT emits a lot of greenhouse gases and contributes to climate change. Businesses must track and reduce their emissions, as well as other toxic electronic waste products that pollute the environment.
- Compliance. Businesses are increasingly under pressure from governments and the public to reduce their environmental impact. Green IT makes more efficient use of resources, reducing waste and emissions and improving recycling rates. This helps businesses comply with government regulations.
- Competitive advantage. Businesses use environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting to disclose green IT practices. Positive ESG is attractive to customers, talent and investors. Most IT organizations include ESG as a purchasing criterion when choosing information and communication technology
Benefits of green IT
Green IT offers the following social, environmental and business benefits:
- Reduced emissions. Decreasing carbon emissions helps improve the environment. To limit global warming, emissions must be reduced by 7.6% every year to 2030, according to the United Nations.
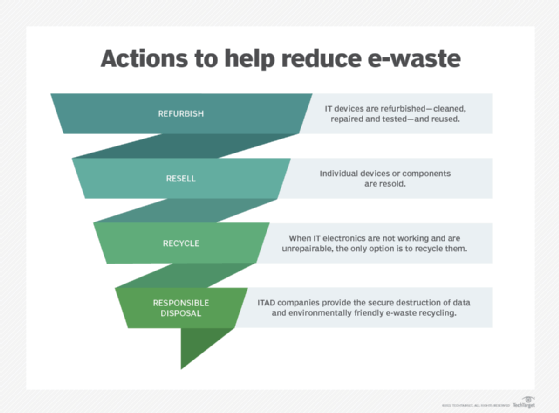
- Less waste. Reusing and refurbishing IT equipment is a cheaper, environmentally friendly equipment acquisition option. It’s also part of the circular economy, which eliminates waste and improves supply-chain resiliency. The circular economy — also known as servitization — is where companies sell products as a service and manage the maintenance and end-of-life processes.
- Extended maintenance periods. Reusable, green IT products allow for longer maintenance cycles and less frequent device replacement.
- Cost savings. Using energy efficient technology to reduce energy consumption helps a business reduce its energy bill and carbon footprint.
- Raised awareness. By using green IT methods and reporting on their use, businesses set an example in their industries and foster collaboration with other companies on climate initiatives.
- Improved corporate culture. Green IT demonstrates to employees that they work for an ethical company, which can improve employee morale and retention. The process increasing sustainability also presents more efficient ways of working.
- Having green IT goals encourages companies to design environmentally friendly technologies and approaches.
- Improved reputation. Green technology use creates a good public image, improving a company’s brand perception.
- Customer satisfaction. Many customers want to do business with socially responsible companies that make sustainability a key part of their strategies.
Challenges of green IT
There are many potential barriers to implementing green IT successfully:
- Cost. The initial cost of implementing new green technologies and programs can be expensive. Revamping old legacy technology systems can also be costly.
- Cultural pushback. Implementing green IT may mean finding new ways of working, which might meet internal resistance and issues with customers.
- Prioritization. It can be difficult to decide where to start implementing green IT. At every level, IT uses energy, so it can be hard to pick which system to address first.
- Conflicting initiatives. In some cases, technology that purportedly reduces emissions can also have a negative environmental impact. Virtualization and artificial intelligence (AI) are examples of technology that can both help and hurt sustainability goals. For instance, AI provides detailed insight into energy use, but AI technology also consumes a lot of energy.
- Emerging fields. Some areas of green tech are relatively new and have few best practices. Green software is one of these emerging fields.
Impact of existing technologies on the environment
Different types of IT hardware negatively affect the environment at various points in their lifecycle:
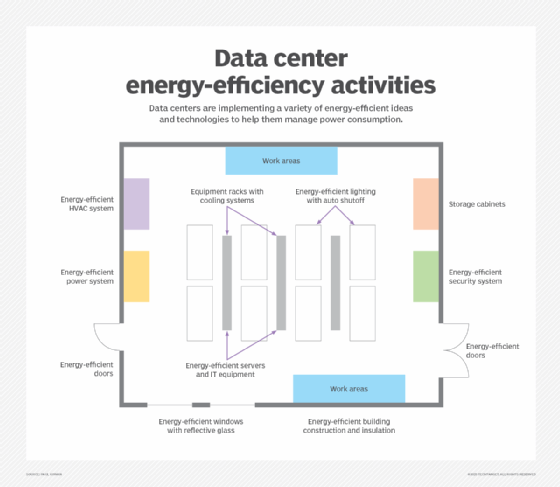
Data center. Organizations commonly seek to use less energy and cut emissions in their data center equipment. In addition to the IT equipment, data centers have extensive lighting, security, HVAC and power management equipment.
Networking equipment. Routers, switches and servers consume energy to store and send information and communications over a network.
Data storage. Data may take multiple trips over various networks before it reaches its storage location. Each trip and the storage itself require energy. Data storage can also be inefficient. For example, Isolated data storage repositories sometimes unknowingly duplicate data, creating data storage waste. A significant portion of an organization’s data may be redundant, obsolete or trivial, also wasting energy.

End-user devices. Most companies have more end-user devices than other equipment in their on-premises facilities. As a result, desktop computers, laptops, smartphones and other devices contribute more to carbon emissions than data centers. End-user devices are also disposed of and replaced more frequently than data center equipment.
Chips. Computer chips consume energy, with some consuming excessive amounts. For example, graphics processing units, used for AI and machine learning workloads, consume up to ten times as much power as central processing units.
Software. Software affects the environment as well. For example, applications that transmit large amounts of data over the network use significant energy. Certain features — like loops — in code are less efficient than other programming methods. Reusable code is a green software alternative that generates energy savings.
Artificial intelligence. AI and machine learning are computationally intensive technologies with high carbon footprints.
Cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency mining is resource intensive. Crypto-assets use a significant portion of global electricity — on par with the total annual energy use of traditional data centers worldwide and the total energy consumption of some countries.
Technologies that are bad for the environment can also be used to improve sustainability efforts. For example, AI monitoring tools can be used to quantify energy use data as well as reduce overall consumption and emissions.
How to reduce environmental impacts
There are many ways to reduce the environmental impact of IT assets, including the following:
- Measure direct impact. IT systems are complex and managing their impact requires accountability, which is only possible with monitoring. Monitoring tools are used to get information on the energy use and other sustainability metrics. For example, use smart sensors to companies can track their data center power usage effectiveness (PUE) and greenhouse gas emissions as well as enable a green data center. Cloud providers offer tools to track power use that users can access from dashboards.
- Measure indirect impact. When measuring carbon emissions, companies should consider their entire supply chain, including their eco-friendliness of providers and partners. IT admins can check partner sustainability levels through nonprofits such as CDP Worldwide and RE100. Companies such as Sustainalytics provide products to measure carbon footprints and other environmental metrics.
- Set goals. There are several frameworks, standards and regulations that IT organizations can use to optimize their eco-friendly For instance, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol standardizes how organizations report and categorize emissions. The National Institute of Standards and Technology SP 800-88 “Guidelines for Media Sanitization” guides companies in proper destruction of data and storage media.
- The Climate Neutral Data Centre Pact aims to make European data centers climate neutral by 2030. It sets aggressive annual PUE targets for data centers and renewable energy goals. Data center operators and trade associations participate. U.S. data centers partner with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to identify green power products.
- Embrace hybrid and remote work. Working remotely decreases the emissions from commuting to an office and the office facilities’ energy requirements.
- Use virtualization. Virtualization saves energy by decreasing the number of physical servers needed.
- The EPA provides a list of certified electronics recyclers meet high environmental standards and safely manage used electronics businesses can use.
- Power management. Hard drives, displays and other components and devices can be set to power down after a certain amount of inactivity to reduce their energy consumption.
- Alternative energy. Geothermal cooling and wind and hydroelectric power are greener alternatives to traditional fossil-fuel energy sources.
- Green design. Products that are optimized for the circular economy and servitization conserve energy, eliminate e-waste and have longer life spans.
The future of green IT
Green IT will continue to gain attention as executives, employees, investors and customers recognize the serious consequences of climate change and understand that environmental sustainability is an important area of investment.
Environmental sustainability concerns are becoming increasingly important. The annual “Gartner 2022 CEO and Senior Business Executive Survey” included environmental sustainability as a top 10 priority for the first time. Survey respondents disclosed that environmental sustainability and ESG serves as competitive differentiators that can attract customers, talent and investors.
A 2022 — “The Role of ESG Programs in IT Decision Making” — from the Enterprise Strategy Group revealed that ESG and sustainability is now an IT purchasing criteria. Eighty-five percent of respondents said they had passed on potential suppliers at least once due to ESG-related concerns.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission recently proposed a rule that would require publicly traded companies to disclose information about their direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions. This rule will likely generate interest in green computing as companies update IT infrastructure to limit emissions.
Some leaders in the IT sector have taken steps to be greener. Leading cloud providers AWS, Google and Microsoft have committed to reduce their carbon footprints and provide green cloud offerings:
- Amazon AWS said it will have 100% renewable power by 2025. It also joined the Climate Neutral Data Centre Pact alongside Google and Microsoft.
- Google’s cloud platform has been carbon neutral since 2007 and using totally renewable power since 2017. In 2019 the company diverted nearly all its data center operations waste from landfills and intends to have entirely carbon neutral data centers by 2030. Google offer its Carbon Sense software, which lets users monitor their carbon emissions.
- Microsoft’s Azure has been carbon neutral since 2012 and aims for 100% renewable-powered data centers by 2025, with plans to be carbon negative by 2030. It also expects to remove all carbon created by its energy use by 2050.
New environmental regulations are being developed as well, such as the European Union’s proposed AI Act. It includes environmental sustainability in the assessment of AI systems. However, some experts believe the act doesn’t go far enough in addressing environmental impact of AI and the low-efficiency chipsets it relies on. They also claim a lack of data surrounding AI, cloud computing and bitcoin make regulation difficult.
Mitigating energy consumption in the data center is a significant part of the green IT movement. Use this template to estimate server power consumption per rack.